Learn about K2 Think — a 32B-parameter open-source AI reasoning model by MBZUAI & G42. Understand its architecture, strengths, challenges, and how it’s changing the AI landscape.
K2 Think: The Open-Source AI Reasoning Engine
Overview
K2 Think is a recently launched open-source AI reasoning model built by the Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI) in collaboration with G42. With just 32 billion parameters, it aims to rival much larger models in reasoning and logical tasks.
K2 Think’s release is significant for a few reasons:
- It emphasizes parameter efficiency — doing more with fewer resources.
- It’s designed for reasoning tasks (math, logic, science) rather than general-purpose chat.
- It supports transparent research — weights, training data, and code are openly released for scrutiny and community extension.
Technical Readers: Architecture, Innovations & Benchmarks
The Six Pillars of K2 Think
K2 Think’s design rests on six interconnected techniques to balance reasoning performance and resource efficiency.
- Long Chain-of-Thought Supervised Fine-Tuning (CoT SFT)
The model is trained with explicit, step-by-step reasoning traces so it learns to break down complex problems internally. - Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR)
After SFT, the model is fine-tuned via reinforcement learning where the reward is based on verifiable success (i.e. correct reasoning outcomes). - Agentic Planning Before Reasoning
Before diving into the solution, K2 Think may break down a problem into subproblems — akin to human planning before solving. - Test-Time Scaling / Adaptive Inference
At inference, it adapts compute based on the problem difficulty (for example, exploring multiple reasoning paths). - Speculative Decoding
This speeds up output generation by speculating ahead on tokens, reducing latency. - Inference-Optimized Hardware Integration
Designed to run efficiently on high-throughput hardware — especially Cerebras wafer-scale engines — enabling its high token throughput.
Together, these pillars make K2 Think “parameter-efficient” — achieving performance comparable to much larger models.
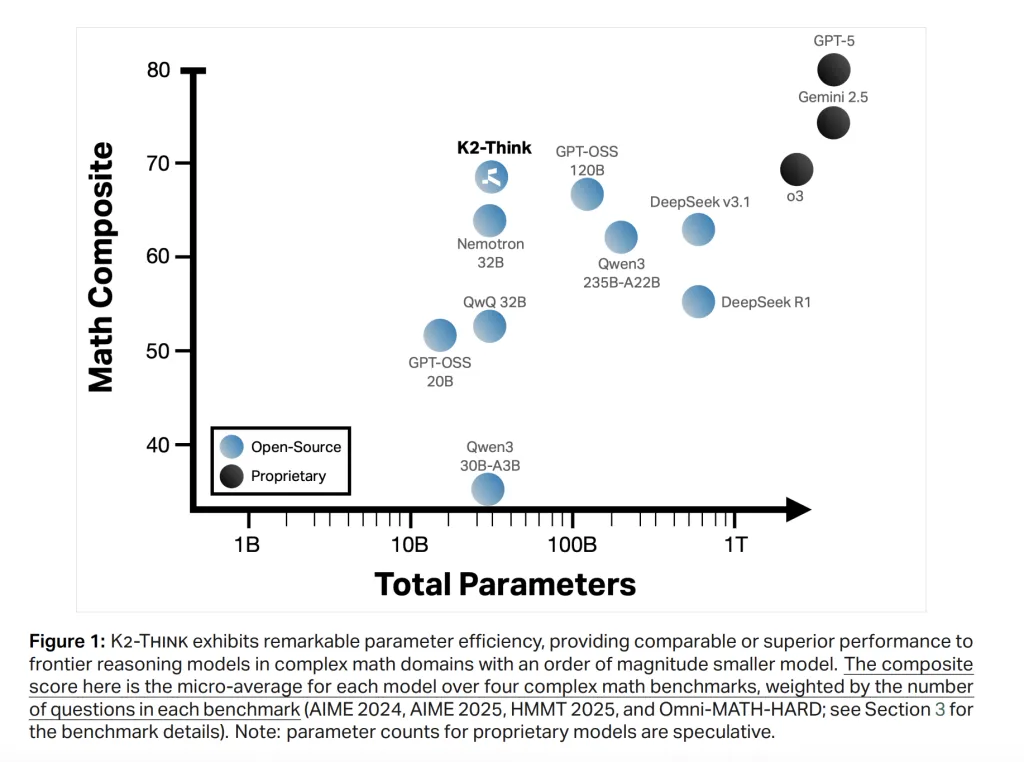
Benchmark Performance
- On mathematical reasoning, K2 Think leads open models across AIME ’24/’25, HMMT ’25, OMNI-Math-HARD.
- In code and scientific tasks, it performs competitively with larger systems in code benchmarks and science reasoning.
- Inference speed: Deployed on Cerebras hardware, it achieves ~2,000 tokens per second, outperforming many GPU setups by a factor.
Strengths & Opportunities
Strengths:
- High performance with fewer parameters → lower cost, less compute.
- Open and transparent — fosters auditability, reproducibility.
- Strong for structured reasoning, mathematical tasks.
- Designed for hardware efficiency.
Challenges / Risks:
- The transparency itself can be exploited in jailbreak/security attacks. Some published reports indicate vulnerabilities shortly after release.
- Performance in looser, more creative or conversational tasks may lag behind massive generalist models.
- Dependence on specialized hardware; on typical hardware, performance might degrade.
- Community maturity, tooling, adoption and integration in real systems remain to be proven.

For Non-Technical Audiences: What Makes K2 Think Special?
Imagine an AI that can think step by step, much like a person solving a math problem on paper, rather than giving a quick guess. That is the idea behind K2 Think.
- It’s open: All the “brains” (weights), training data, and software are shared publicly.
- It’s efficient: It uses much less “brain power” (parameters) yet competes with giants.
- It’s fast: When run on special hardware, it produces answers quickly — thousands of words per second.
- It’s smart: Instead of just generating text, it reasons — doing math, logic, and structured thinking better than many models twice its size.
So, for students, educators, developers, or businesses that need reliable logical reasoning (say, solving equations, planning complex steps, or making scientific inferences), K2 Think offers a powerful, accessible tool.
However, it’s not perfect. Because everything is transparent, some creative attackers have already tried (and reportedly succeeded in) bypassing its safety filters. Also, in open conversation, storytelling, or casual chat, it may not feel as fluent as models built for general language tasks.
Use Cases & Applications
- Math tutoring & problem solving
- Scientific reasoning assistants
- Logic engines in research tools
- Decision support systems
- Explainable AI & research tools
- Hybrid systems / modular architectures
Because it is open and transparent, researchers and developers can adapt and extend K2 Think into domain-specific reasoning systems.
How This Changes the AI Landscape
- Beyond scale → smarter design
K2 Think challenges the notion that “bigger equals better.” It shows smaller models, with clever enhancements, can compete. - Democratizing AI reasoning
Open-source reasoning lowers the barrier to advanced models. More people can study, adapt, and integrate powerful reasoning engines. - Geopolitical & regional AI leadership
The UAE, via MBZUAI and G42, is staking a claim in frontier AI, showing that innovation is global. - New challenges in safety & transparency
As transparency improves trust, it also gives adversaries insight into internal mechanisms. Developing robust safeguards in open models is critical.
