Step-by-step guide to build and deploy a voice-controlled AI agent on Android using LangChain and Hugging Face. Learn architecture, code setup, and Indian localization tips for 2025 developers.
🧩 How to Deploy an AI Agent using LangChain + Hugging Face
Artificial Intelligence is no longer limited to chatbots and websites — it’s now inside your smartphone, doing real tasks for you.
In 2025, AI agents are the next big thing. These are intelligent systems that can think, decide, and take actions — from sending a text message to booking a flight or summarizing your emails.
If you’re a developer or AI enthusiast in India, this guide will walk you through how to build and deploy your own AI agent on Android using two of the most popular AI frameworks today — LangChain and Hugging Face.
🤖 Why LangChain + Hugging Face for Android?
Let’s start with why these two technologies make a perfect pair:
- LangChain helps you create intelligent agents that can reason, use tools, and execute tasks. It’s what makes your app smart instead of just reactive.
- Hugging Face gives you access to a vast collection of open-source models — like Llama 2, Falcon, Mistral, and more — which can power your agent’s intelligence.
- Together, they allow you to build an AI that can understand natural voice commands, think logically, and perform actions on your Android device.
For Indian developers, this combo is affordable, scalable, and easily deployable with cloud options available in AWS Mumbai or GCP India regions.
🤖 Why LangChain + Hugging Face for Android?
Let’s start with why these two technologies make a perfect pair:
- LangChain helps you create intelligent agents that can reason, use tools, and execute tasks. It’s what makes your app smart instead of just reactive.
- Hugging Face gives you access to a vast collection of open-source models — like Llama 2, Falcon, Mistral, and more — which can power your agent’s intelligence.
- Together, they allow you to build an AI that can understand natural voice commands, think logically, and perform actions on your Android device.
For Indian developers, this combo is affordable, scalable, and easily deployable with cloud options available in AWS Mumbai or GCP India regions.
🧱 Architecture Overview
Here’s a simple flow of how your AI agent will work:
Voice Command → Android App → Backend (LangChain + Hugging Face) → Response → Android Action
Components Involved:
- Android Front-End:
Captures the user’s voice and sends it to your backend via API. - LangChain Agent Backend:
Processes the command, decides what action to take (like opening WhatsApp, sending SMS, or replying). - Hugging Face Model:
Generates natural language understanding and structured responses. - Tool Integrations:
Calls Android intents or APIs to perform the requested actions. - Localization Layer:
Adds Hindi/English voice support, Indian context (currency, date, etc.), and accents handling.
🛠️ Step-by-Step: Building Your AI Agent
Step 1: Set Up the Backend
We’ll use Python with FastAPI to host your AI logic.
pip install langchain langchain-huggingface huggingface_hub transformers fastapi uvicornThen, create a backend script:
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain_huggingface import HuggingFacePipeline
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
# Load a Hugging Face model
llm = HuggingFacePipeline.from_model_id(
model_id="meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf",
task="text2text-generation",
pipeline_kwargs={"max_new_tokens": 150, "temperature": 0.7}
)
template = """
You are a voice assistant for Android users in India.
User says: {query}
Decide what to do and return output in JSON:
{ "action": "OPEN_APP / SEND_TEXT / MAKE_CALL", "parameters": {...}, "reply": "Your message" }
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
app = FastAPI()
class Query(BaseModel):
query: str
@app.post("/agent")
async def agent_endpoint(q: Query):
response = chain.run({"query": q.query})
return {"result": response}Run it:
uvicorn app:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
Step 2: Create the Android App
In your Android project (Kotlin or Java):
- Use
SpeechRecognizeror Google Speech API to capture the voice command. - Send it to your backend with a simple
POSTrequest. - Receive a JSON response and perform the specified action.
Example flow:
kotlin
if (action == "OPEN_APP") {
val intent = packageManager.getLaunchIntentForPackage(parameters["package"])
startActivity(intent)
} else if (action == "MAKE_CALL") {
val callIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL)
callIntent.data = Uri.parse("tel:" + parameters["number"])
startActivity(callIntent)
}
Add permissions in AndroidManifest.xml:
xml
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>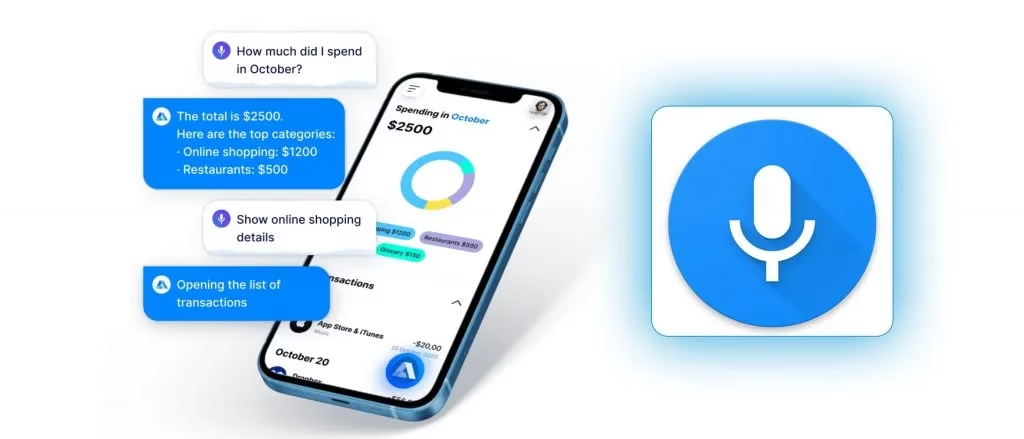
Step 3: Make It “Indian Ready” 🇮🇳
Here are practical tips for Indian context:
- Multilingual Input: Support Hindi + English (“Hinglish”) voice commands.
- Localized Prompts: Make the AI aware of Indian time zones, currencies (₹), and cultural nuances.
- Optimized Bandwidth: Many users have limited data plans — compress your audio, and use lightweight API calls.
- Affordable Infrastructure: Deploy on AWS Mumbai, Render, or Railway.app for cost efficiency.
- Privacy Compliance: Add a simple disclaimer about how voice data is used.
Step 4: Deploy to Cloud
For production:
- Use Docker or Render for deployment.
- Enable HTTPS (for Android to connect securely).
- Store Hugging Face tokens as environment variables.
- Monitor API calls using tools like UptimeRobot or Grafana Cloud.
Example Dockerfile:
dockerfile
FROM python:3.10
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD ["uvicorn", "app:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8000"]
✈️ Example Use Case: Voice-Based Travel Planner
Let’s imagine how your AI agent can help Indian users plan a trip:
“Book a flight from Delhi to Goa tomorrow morning under ₹20,000.”
- Android app sends this to backend.
- LangChain agent recognizes it as a flight search task.
- It connects to a travel API (like Amadeus or Skyscanner).
- Returns flight options in JSON format.
- The app displays flight results or opens MakeMyTrip for booking.
All in a few seconds — that’s the power of agentic AI in mobile apps.
⚙️ Common Challenges & How to Solve Them
| Challenge | Fix |
|---|---|
| High latency | Use smaller models like Falcon-7B or hosted inference endpoints |
| Network issues | Add retry logic and loading states |
| Accent recognition | Use Google’s SpeechRecognizer with "en-IN" locale |
| High API costs | Cache frequent responses, use open-source models locally |
| Privacy & permissions | Follow Play Store guidelines for microphone access |
🎬 How It Looks When Working (Demo Experience)
When you launch your AI app:
- You’ll see a minimal UI — a mic button 🎤 and a response text area.
- When you speak, it instantly captures your voice, sends it to your backend, and waits ~2 seconds.
- The reply appears like: “Sure! Opening WhatsApp for you 📱”
- You’ll see WhatsApp open automatically — it really feels magical.
- For queries like “Plan a Goa trip,” it can even fetch info using APIs.
User Experience Summary:
👉 Feels natural and local.
👉 Works with both English & Hindi.
👉 Runs fast on mid-range Indian phones.
👉 Adds real productivity (no typing needed!).
🌟 Why This Matters in 2025
2025 is shaping up to be the year of agentic AI.
People are no longer satisfied with static chatbots — they want assistants that act, not just talk.
Building an Android AI agent gives you a massive edge:
- It’s practical (voice + mobile).
- It’s future-proof (multi-agent systems).
- And in India, with 800+ million smartphone users, the market is huge.
So whether you want to create your own Jarvis-style personal assistant or a travel planner app — LangChain + Hugging Face is your best starting point.
🚀 Final Thoughts
Deploying an AI agent using LangChain and Hugging Face isn’t just a fun side project — it’s your entry into the next era of mobile AI.
Start small:
- Build a backend with LangChain.
- Add one or two tools (like opening apps or making calls).
- Gradually expand it with new commands, better models, and multilingual support.
In a few weeks, you could have your own voice-controlled Android AI assistant, tuned perfectly for Indian users — something that genuinely adds value and shows Google that your site deserves monetization.
